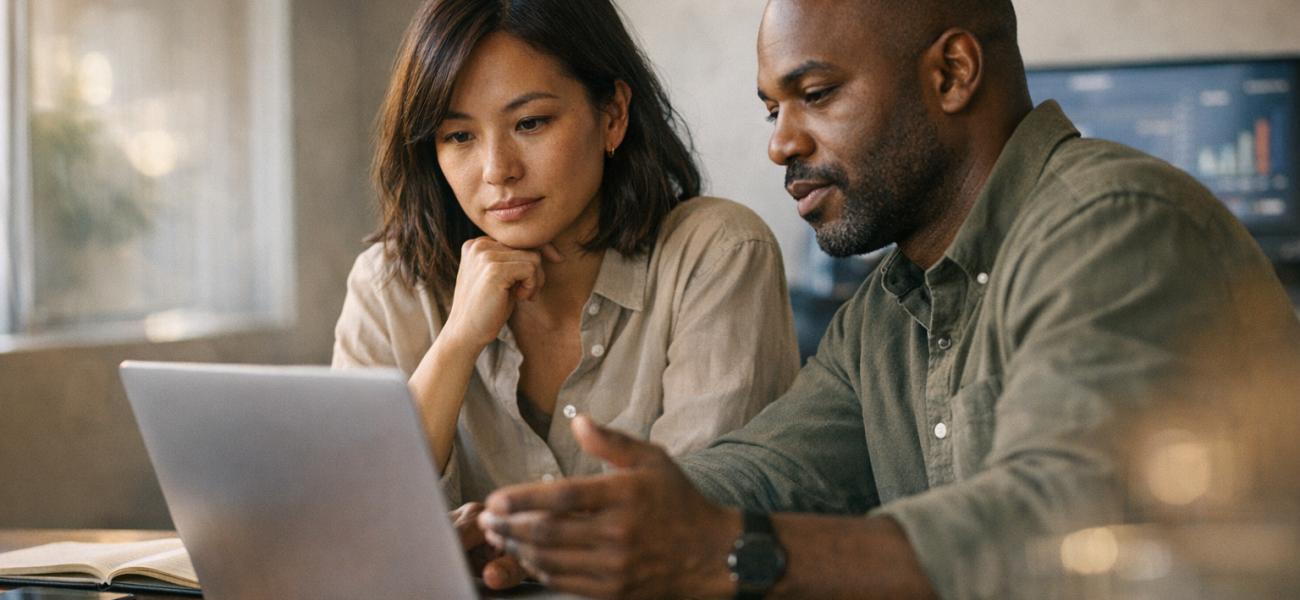
AI brand recommendations have become common tools for consumers and marketers, yet their reliability and consistency remain under-explored. This article focuses on the inconsistency of brand or product recommendations generated by popular AI systems such as ChatGPT, Claude, and Google’s AI, and outlines practical approaches for marketers to measure visibility more accurately.
Understanding Variability in AI Brand Recommendations
Large language models behind AI recommendation engines operate on probabilistic processes, which inherently generate diverse outputs even with the same input. Unlike traditional search engines that strive for consistent ranking, these AI systems deliver different brand lists every time they are prompted. This is not a flaw but a deliberate design feature enabling variability in responses.
In an extensive study involving 600 volunteers running nearly 3,000 prompt iterations, results showed that obtaining the exact same brand list twice had less than a 1% chance, and identical ordered lists appeared at closer to 0.1%. The length of recommended brand lists also fluctuated significantly, from a few options to over ten in some cases.
Why Rankings Fail in AI Recommendations
Traditional SEO and brand monitoring rely heavily on ranking positions to assess visibility and consumer behavior. However, with AI-generated brand recommendations, rank positions are unstable and unreliable. Any attempt to quantify brand standings in AI outputs using fixed ranks is likely misleading.
“Marketers must recognize that AI-generated recommendations do not function like static search results; rank volatility renders traditional position tracking ineffective,” explains Dr. Lena Meyers, a marketing technology expert.
Visibility Percentage as a Reliable Metric
Despite chaotic rankings, a metric called ‘visibility percentage’ emerges as a more stable indicator. This metric tracks how often a brand appears across multiple AI-generated lists regardless of position. Brands frequently mentioned can maintain visibility percentages of 60% to 90% in repeated tests, signifying strong AI-recognized presence.
For example, hospitals or consumer brands identified repeatedly show meaningful visibility despite fluctuating positions. This suggests that monitoring brand appearance frequency provides better insights than focusing on AI rank order.
Market Size Effects on AI Recommendations
Market characteristics influence recommendation stability. Smaller or niche markets typically yield more consistent AI outputs concentrated around known providers. By contrast, broad markets with many competitors generate fragmented and highly variable brand lists.
For instance, regional service providers or specialized B2B tools see AI recommendations clustered tightly, while large categories such as novels or creative agencies experience scattered brand suggestions with little consensus.
The Role of User Prompts in AI Brand Suggestions
User input phrases have tremendous variation. A compilation of real-world prompts shows low semantic similarity even for identical underlying requests. Surprisingly, AI systems can still extract core intent and supply similar brand sets despite this diversity, highlighting robust intent recognition capabilities.
For example, headphone recommendations across hundreds of varied prompts consistently include top brands like Bose, Sony, Apple, and Sennheiser. Shifting the intent keyword from general listening to gaming or noise canceling appropriately alters the brand roster, demonstrating intent sensitivity.
Challenges in Prompt Standardization
The chaotic nature of human language introduces complexity in brand tracking. Because no two prompts are exactly alike, capturing an intent comprehensively requires aggregating many diverse user inputs. This diversity adds a layer of complexity but ensures that AI captures broad market nuances.
“The implication for marketers is that they must monitor AI responses at scale rather than relying on single or few queries,” notes Daniel Ortiz, AI and consumer behavior analyst.
Practical Recommendations for Marketers
Given the inconsistent nature of AI brand recommendations, marketers should adjust their measurement frameworks:
1. Favor Visibility Over Rank
Track how often a brand is mentioned across multiple queries and runs to obtain a statistically meaningful visibility measure, rather than focusing on rank positions that fluctuate randomly.
2. Use Many Prompts and Runs
Employ varied prompts reflecting different user phrasings and perform repeated runs to average out randomness and better reflect true brand presence.
3. Adapt to Market Size
Understand that smaller, niche markets are less volatile and can yield more stable brand visibility data, while huge, competitive categories require more extensive sampling and nuanced interpretation.
4. Combine Visibility Metrics with Qualitative Insights
Couple quantitative AI visibility data with market research and customer feedback for a more comprehensive assessment of brand positioning and perception.
Open Questions and Future Directions
Despite advancements, questions remain about the optimal number of prompt iterations, the representativeness of API queries compared to real users, and the best methods for prompt selection to reflect market demands.
Answering these questions will enable marketers to harness AI-powered recommendations more effectively and to refine their competitive intelligence efforts.
Conclusion
AI brand recommendation systems exhibit high variability and randomness, making traditional rank-based performance tracking ineffective. However, measuring brand visibility frequency through multiple queries provides meaningful insights that can inform marketing strategies. Marketers must embrace new metrics and scalable monitoring to navigate the unpredictability of AI-generated brand insights.